How does sublimation paper work?
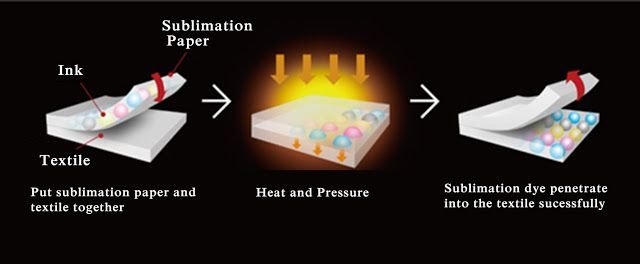
While the sublimation process is slightly more complex than heat transfer, it yields impressive results. The process of transferring a design from sublimation paper, printed with sublimation ink, to a substrate involves the following steps:
- Apply heat to turn the ink into a gas.
- The gas then penetrates the surface of the substrate, creating a vibrant and long-lasting print.
- This process is most effective on polyester-based or poly-coated materials.
Before being heat pressed onto the substrate, the ink on the sublimation paper dries quickly and the printed image is mirrored to ensure accurate design transfer. During the sublimation process, the solid ink bypasses the liquid phase and directly becomes a gas under heat and pressure, enabling it to permanently bind to the material.
This whole process contributes to the creation of designs that are not just prints on the material but become a part of the material itself, leading to an unbeatable durability and vibrancy.
How does heat transfer paper work?
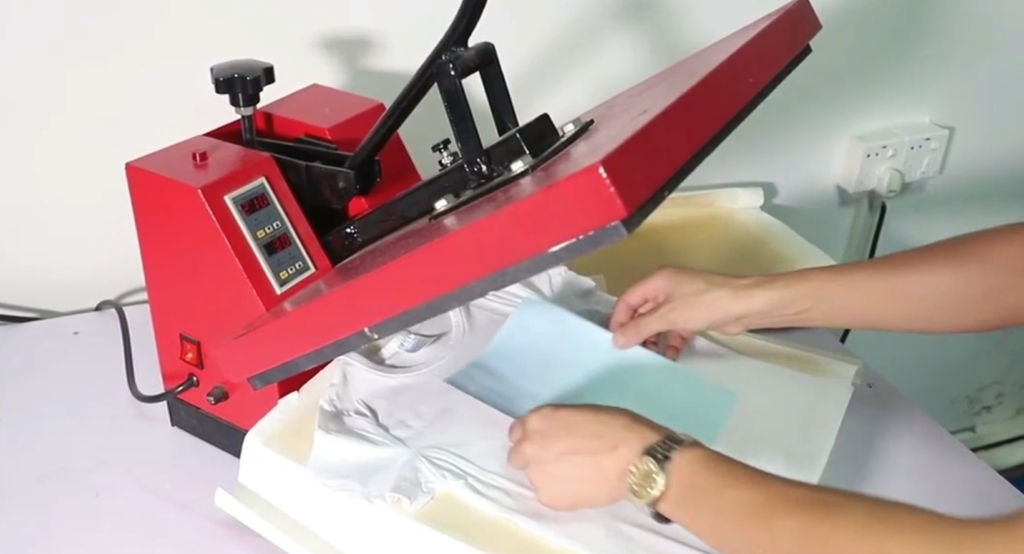
Heat transfer printing is a process where a design is printed onto specially coated paper and then transferred to a garment using a heat press machine that applies heat and pressure. This process can be performed using either a laser or inkjet printer, offering flexibility based on your available resources.
The flexibility of heat transfer paper in garment printing is significant. It can be used on a variety of fabrics such as cotton, polyester, and blended materials, making it a versatile option for garment printing. Notably, heat transfer printing can accommodate a wide range of designs, including graphics, text, and even high-resolution photographs.
For light-colored heat transfer paper, images must be mirrored before printing, while dark-colored heat transfer paper does not require this. Moreover, when using heat transfer paper on cotton items, a special coating is necessary to ensure the durability of the print.
Surely, heat transfer paper has its nuances, but its versatility and accessibility make it a popular choice in the world of garment printing.

The fundamentals of sublimation paper
Sublimation paper printing is a process where dye-based inks are transformed into gas through heat. This allows the ink to infuse directly into specially coated polyester or poly-coated substrates. Here are the key points:
- How It Works: Under the heat and pressure of the heat press, the sublimation ink changes from a solid state (the ink consists of pigment particles and is therefore solid) to a gaseous state. The gas then penetrates the surface of the material and permanently bonds with the fibers.
- Result: The final image is vivid and durable because the dye becomes part of the fabric or surface rather than just sitting on top.
- Best For: Items like polyester apparel, ceramic items with polymer coatings, and other substrates designed to accept sublimation inks.
Exploring heat transfer paper printing
Heat transfer paper printing is known for its flexibility and lower entry cost, making it a popular choice for many home and small-scale operations.
- Process Overview: In this method, designs are first printed onto a specially coated transfer paper using a laser or inkjet printer. When pressed onto the target material under heat, the image adheres to the surface.
- Flexibility: Unlike sublimation, heat transfer can be used on a variety of fabrics, from cotton to blended materials. However, the ink typically remains on the surface rather than becoming embedded.
- Considerations: For optimal results on light-colored items, images are often mirrored before printing. Darker substrates may require a white base layer to enhance vibrancy.
Sublimation paper vs heat transfer paper key comparisons
When deciding between sublimation and heat transfer printing, several factors come into play:

Startup and operational costs
- Sublimation paper:
- Equipment Needs: Requires a dedicated sublimation printer, specialized inks, and a heat press.
- Cost Outlook: Although the initial investment is higher, ongoing costs tend to be lower, making it an economical choice for high-volume production.
- Heat transfer paper:
- Equipment Needs: Works with standard inkjet or laser printers.
- Cost Outlook: Lower startup costs are attractive for beginners, but the per-item cost may increase over time due to more expensive transfer paper and potential reprints.
Material and fabric suitability
- Sublimation paper:
- Ideal Fabrics: Best for high polyester content or surfaces pre-coated with polymers.
- Durability: The dye bonds with the material, leading to prints that resist fading and peeling over time.
- The substrate is suitable for light colors: Sublimation paper is more suitable for transferring on light-colored substrates, dark colors less so.
- Heat transfer paper:
- Versatility: Compatible with a broader range of fabrics, including cotton.
- Limitations: Prints may not be as long-lasting on certain materials, and care must be taken during washing to avoid cracking or fading.
- Compatible with both dark and light colors: There is no restriction on whether the substrate is dark or light colored, as long as the corresponding paper is used.
Image quality and longevity
- Sublimation Printing:
- Image Integrity: Produces smooth gradients and high-definition images, making it perfect for intricate designs and photography.
- Durability: As the ink becomes part of the substrate, the prints maintain their vibrancy even with frequent use.
- Heat Transfer Printing:
- Image Details: Capable of high-quality prints, though the ink sits on the surface.
- Maintenance: May require special care, such as washing items inside out or in cold water, to preserve the printed design.
Additional process considerations
- Weeding and Prep Work:
- Heat transfer methods often involve a weeding step—removing excess paper material around the design. This extra labor can be a drawback for detailed or small designs, whereas sublimation printing eliminates this step entirely.
- Technical Nuances:
- Sublimation demands precise control over temperature and pressure settings, while heat transfer printing offers more leeway with everyday equipment. Both methods, however, require consistent maintenance of tools and materials for optimal results.
Choose sublimation paper or heat transfer paper?
When determining the best printing method, consider:
- Budget: Are you ready to invest in specialized equipment, or do you prefer a more accessible, low-cost entry point?
- You can consider heat transfers with a low budget up front, and then learn about sublimation before committing later.
- Heat transfer paper is not too costly to use upfront, sublimation paper requires some investment from the start.
- Material: What substrates will you be printing on? Polyester items are best served by sublimation, whereas cotton may benefit more from heat transfer.
- If it’s all about printing apparel, consider heat transfer paper. If the garments are only a small part, then consider sublimation paper.
- Durability Needs: Do you require prints that will withstand frequent washing and handling? Sublimation generally offers better longevity.
- When durability is a priority, sublimation paper is definitely the way to go.
Conclusion
Both sublimation and heat transfer printing have distinct advantages. Sublimation is ideal for those seeking permanent, vibrant images that meld into the fabric, while heat transfer printing offers flexibility and lower startup costs for a variety of materials. Understanding your project’s needs—ranging from material type to budget—will help you make an informed decision and achieve outstanding results.









